|
US
Navy Aircraft Designations 1911-1962
Part
One
by
Stephane Wrobel
This series describes how the U.S. Navy names its planes.
In the United States, aircraft designations have changed across the years depending on
the function the aircraft performed. The functions have evolved with time and technology.
In the early years of aviation, there were only a few manufacturers. The US Naval
General Staff therefore first described aircraft primarily according to their function.
E a r l y
Y e a r s ( 1 9 1 1 - 1 9 3 3 )
|
The US Navy was born in 1911 and with it, the need to label its aircrafts.
From 1911 to 1914, designations were based on a letter which indicated the
manufacturer and a number which described the aircraft's general type.
A = Curtiss hydroaeroplanes
B = Wright hydroaeroplanes
C = Curtiss flying boats
D = Burgess flying boats
E = Curtiss amphibious flying boats
It can be seen that there were only three manufacturers. This explains why the mission
was emphasised rather than the manufacturer.
In March 1914 a new designation system was issued. The designation was now made of two
letters denoting the type, and one number denoting the type in Navy inventory.
"A" type stood for all "heavier than air" and within this category
several different subtypes which were the following :
L = land machines
H = hydroaeroplanes
B = flying boats
X = amphibious
C = convertibles (could be equiped as amphibious type).
The "D" type was for Airships and dirigibles, "B" for balloons and
"K" for kites.
From 1923 to 1962, the system was complicated by introducing a letter for the
manufacturer and a version/modification number.
Here are the four major elements :
- Aircraft Type/Class letter
- Manufacturer type number
- Manufacturer letter
- Version number
In 1940, a third type was introduced to cover Helicopters : The H type.
In 1945 the K type appeared for pilotless aircraft
The X type was added for experimental aircraft.
The original model type number of a manufacturer is omitted.
For example, the first fighter aircraft built by Grumman was named FF. When the second
release appeared the plane was named FF-2. The second aircraft of the type from Grumman
was then named F2F.
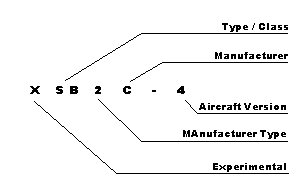
The list below will help you to find the type and the manufacturer of all Navy aircraft
to 1962. Examples of famous aircraft names are provided in italics.
- A = Attack / Ambulance
- B = Bomber (BG-1)
- BT = Bomber Torpedo (BTD-1 Devastator)
- D = Drone
- F = Fighter (F4U Corsair)
- G = Glider / Transport single engine / in flight Refueling (GV-1 Hercule –
KC-130F)
- H = Hospital / Air Sea Rescue / Helicopters (HSS-1)
- J = Utility / Transport (J2F Duck)
- JR = Utility Transport (JRF-1 Goose)
- K = drone (F6F-5K Drone Hellcat)
- L = Glider
- M = Marine Expeditionnary
- N = Trainer (NC-1)
- O = Observation (OU-1)
- OS = Observation Scout (OS2U Kingfisher)
- P = Patrol / Pursuit
- PB = Patrol Bomber (PBY Catalina)
- PT = Patrol Torpedo
- R = Transport / Racer (R4D Dakota)
- S = Scout (SC Seahawk)
- SB = Scout Bomber (SBD Dauntless)
- SN = Scout Trainer (SNJ Texan)
- SO = Scout Observation (SOC Seagull)
- T = Torpedo / Transport / Training (BT-1)
- TB = Torpedo Bomber (TBF Avenger)
- TD = Target Drone
- U = Utility (HUP-3 Retriever)
- W = Warning (WF-2 tracer)
-
As can be seen, a type letter could be used several different ways. This depended on
the period. When a new function appeared the most appropriate letter was used and a new
one was issued if the one was used for another type before. In addition, different letters
could be combined to obtain a plane that can accomplish different missions.
Here are the manufacturers' letters
- A Aeromarine Plane and Motor Co. 1922
- A Atlantic Aircraft Corp (American Fokker) 1927–1930
- A Brewster Aeronautical 1935–1943
- A General Aviation Corp (ex Atlantic) 1930–1932
- A Noorduyn Aviation, Ltd. (Canada) 1946
- B Beech Aircraft Co. 1937–1962
- B Boeing Aircraft Co. 1923–1962
- C Cessna Aircraft Corp. 1943–1951
- C Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Co. 1922–1946
- C Curtiss Wright Corp 1948–1962
- C DeHaviland Aircraft of Canada 1955–1962
- D Douglas Aircraft Co. 1922–1967
- D McDonnell Aircraft Corp. 1942–1946
- DH DeHavilland Aircraft Co. Ltd. (England) 1927–1931
- DW Dayton-Wright Airplane Co. 1923
- E Bellanca Aircraft Corp. 1931–1937
- E Cessna Aircraft Co. 1951–1962
- E Edo Aircraft Corp. 1943–1962
- E Hiller Aircraft Corp. 1948–1962
- E Piper Aircraft Corp. 1941–1945
- F Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corp. 1931–1962
- G Goodyear Aircraft Corp. 1942–1962
- G Great Lakes Aircraft Corp. 1929–1935
- H Hall Aluminum 1928–1945
- H Howard Aircraft Co. 1941–1944
- H McDonnell Aircraft Corp 1946–1962
- J Berliner/Joyce Aircraft Co. 1929–1935
- J North American Aviation 1937–1962
- K Fairchild Aircraft Corp. 1937–1942
- K Kaman Aircraft Corp 1950–1962
- K Keystone 1927–1930
- L Bell Aircraft Corp. 1939–1962
- L Loening Aeronautical Engineering Corp. 1922–1932
- M General Motors Corp. (Eastern Aircraft Div.) 1942–1945
- M Glenn L. Martin Co. 1922–1962
- N Gyrodyne Company of America 1955–1962
- N Naval Aircraft Factory 1922–1948
- O Lockheed Aircraft Corp. 1931–1962
- P Pitcairn Autogyro Co. 1931–1932
- P Piasecki Helicopter Corp. 1946–1955
- P Vertol Aircraft Corp. 1955–1962
- Q Fairchild Engine and Airplane Co. 1928–1962
- R Ford Motor Co. 1927–1932
- R Ryan Aeronautical Co. 1948–1962
- S Sikorsky Aviation Corp. 1928–1962
- S Stearman Aircraft Co. 1934–1945
- T The Northrop Corp. 1933–1937
- T Timm Aircraft Corp. 1941–1943
- T Northrop Aircraft Inc. 1944–1962
- U Lewis & Vought, Chance Vought, 1922–1962
- V Vought Sikorsky
- V Vultee Aircraft Inc. 1943–1945
- V Lockheed Aircraft Corp. 1942–1962
- W Waco Aircraft Corp. 1934–1945
- W Wright Aeronautical Corp. 1922–1926
- W Willys-Overland Co. 1948–1962
- Y Consolidated Aircraft Corp. 1926–1954
- Y Convair Division (General Dynamics Corp) 1954–1962
The list is not complete but the most important manufacturers are listed here.
In the second part of the article, we’ll see how the aircraft designation since
1962 (still in use) and the redesigned code for aircraft in use in 1962. Then you
will understand why a Skyraider is called AD-6 or A-1H.
Happy modeling
Stef
Article Text Copyright © 1998 by Stephane Wrobel
Page Created 02 October, 1998.
Last updated 18 May, 2001.
Back to HyperScale Main Page
Back to the Reference Library
|
Home |
What's New |
Features |
Gallery |
Reviews |
Reference |
Forum |
Search